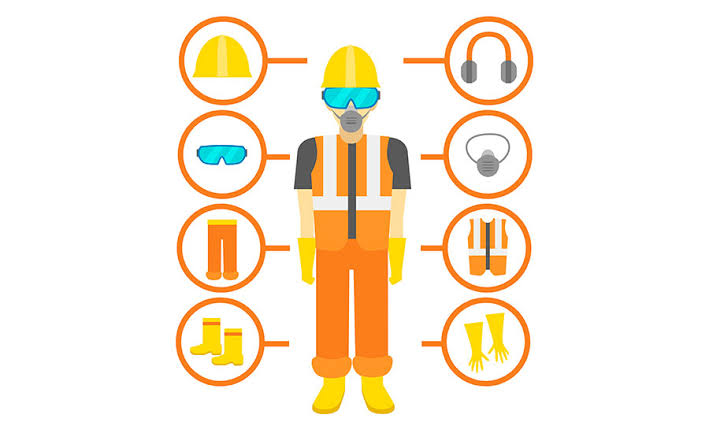
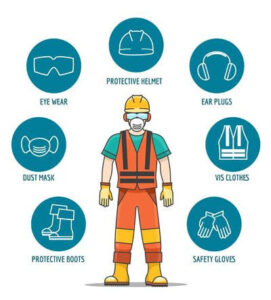
When to and when not to use PPE during HSE operation
The need to know when to use PPE and when not to is very important in HSE. Employers are required to provide and use personal protective equipment (PPE) at work. Today we will be discussing why PPE are very important, how to use them ,when to use them and when not to use them during operations.
This may include items such as helmets, gloves, goggles, visible clothing, safety shoes, and seat belts. Breathing apparatus (RPD) included.
Why is PPE so important?
Improving workplace safety with case studies includes the provision of guidelines, procedures, training and supervision to encourage people to work safely and responsibly. Some risks may persist even with secure engineering controls and operating systems.
This includes damage to the lungs.
– If contaminated air is inhaled into the head and feet, for example
– If substances come into contact with the eyes.
-If particles are blown out or corrosive liquid splashes on the skin, z.
-Contact with corrosive substances in the body, for example, in extr
eme heat or cold. Inthis case, PPE is needed to reduce the risk.
What should I do?
Use PPE only as a last resort. If PPE is still needed after other controls have been introduced (and there may be situations such as head protection on most construction sites), they should be provided to employees free of charge (see selection details below).

Make sure your employees are trained to use them correctly and know how to detect and report bugs. Select and use the following questions.
Who is exposed to whom?
How long have you been exposed? How vulnerable are you? When choosing and using PPE: Choose CE marked products in accordance with the 2018 Personal Protective Equipment Guidelines.
The supplier can inform you. Choose the right equipment for you based on the size, comfort and weight of the PPE. When users help vote, they are more likely to take advantage of it.
Other PPE Suggestions;
Do not allow the use of PPE for work that “only takes a few minutes”. Check with your supplier which PPE is right for you.
Describe the task.
For example, do not use it in a dry, clean cabinet. If it can be reused, it should be cleaned and maintained in good condition. Use replacement parts that match the original.
Take care of the breathing filter, replace the PPE that will be in charge of maintenance and how to do it, and provide suitable disposable clothing suitable for dirty jobs with high washing costs. For example, for visitors who need protective clothing.
Regularly monitor and check the use of PPE.
If not, finding out why there are no safety signs will help remind you that you should wear PPE. Watch for changes in equipment, materials and methods.
Danger of splashing chemicals or metal.Eyes, dust, projectiles, gases and vapors, radiation. Additional goggles, goggles, face shield, face shield, and visor notes may need to be updated to be available for the type of PPE you provided. Has the right combination .
The precise combination of shock / dust / splash / molten metal protects the eyes and adapts well to the head and neck. DANGER Impact from falling or flying objects, risk of head bumping, hair entanglement in machinery, splashing or splashing of chemicals, climatic or temperature safety helmet, hat, head net and firefighter’s helmet.
Some safety helmets may contain or be fitted with specially designed eye or hearing protection. Remember the neck (for example, a scarf).
Ears
Noise is a combination of noise level and exposure time. Extremely high noise levels are dangerous even for a short time. Earplugs, earplugs, half insert / core cap options Note Provide adequate hearing protection for the type of operation and ensure personnel know how to operate Protective devices to ensure safety and communication while reducing noise to an acceptable level Select Risk of wear to hands and arms.
Extreme temperatures, cuts and punctures, shock, chemicals, electric shock, radiation, biological agents and prolonged immersion options Gloves, cuffed gloves, gloves and sleeves covering part or all of the shoulder. Gloves if: Avoid operating such a machine like. You can hold gloves while exercising. Some materials can quickly penetrate chemicals. With this article we have come to understanding of When to and when not to use PPE during HSE operation
HSENations